Stage 1: Business Research
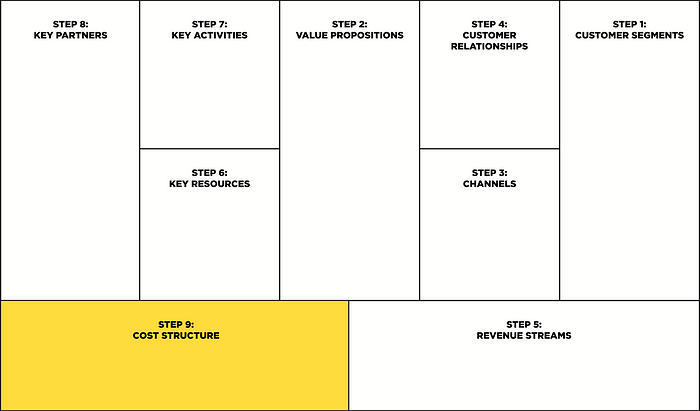
Examples: Business model canvas (BMC)
_
A strategic tool for describing the business model of a new or existing offline business.
The business model logically justifies how the organization creates, provides, and increases value. In other words, it is a description of the logic of actions that lead to profit.
Therefore, it is a template for describing how your company, project, or product creates value and makes money on it.
Modeling is necessary because it solves 3 main tasks: business management, increasing the value of the business and implementing innovation in the business.
The Business model canvas is designed to test the viability of a business idea. The business model canvas was created by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur. The canvas of business model canvas was developed for offline companies.
Startups also became interested in this method and began to apply it too, but it turned out that the business model canvas had sections in which there was nothing to enter, for example, there were no partners or distribution channels in the project, etc.
For startups, you can use the lean canvas, which is a business model canvas but adapted to startups that are at an early stage of development.
Gestalt is a philosophical concept, which in translation means: a holistic image, form, or figure. In psychology, this is the name given to a structure that is perceived by a person as a whole, and not as different elements. For example, we perceive some image, the face of a loved one, a favorite melody, or an abstract idea of a colleague immediately and completely.
The canvas is the gestalt of the business model because it contains all the main elements of the strategy.
Official business model canvas template by Strategyzer
The purpose of the business model canvas
To describe the product or analyze the business model that is already in use from the standpoint of its efficiency and development potential.
Value for the team
The canvas best demonstrates all the aspects necessary to build the most effective strategy.
Value for business
It will help to check the viability of a business idea.
Duration:
- Preparation: up to 30 minutes
- Main activity: from 4 to 8 hours
Creating process:
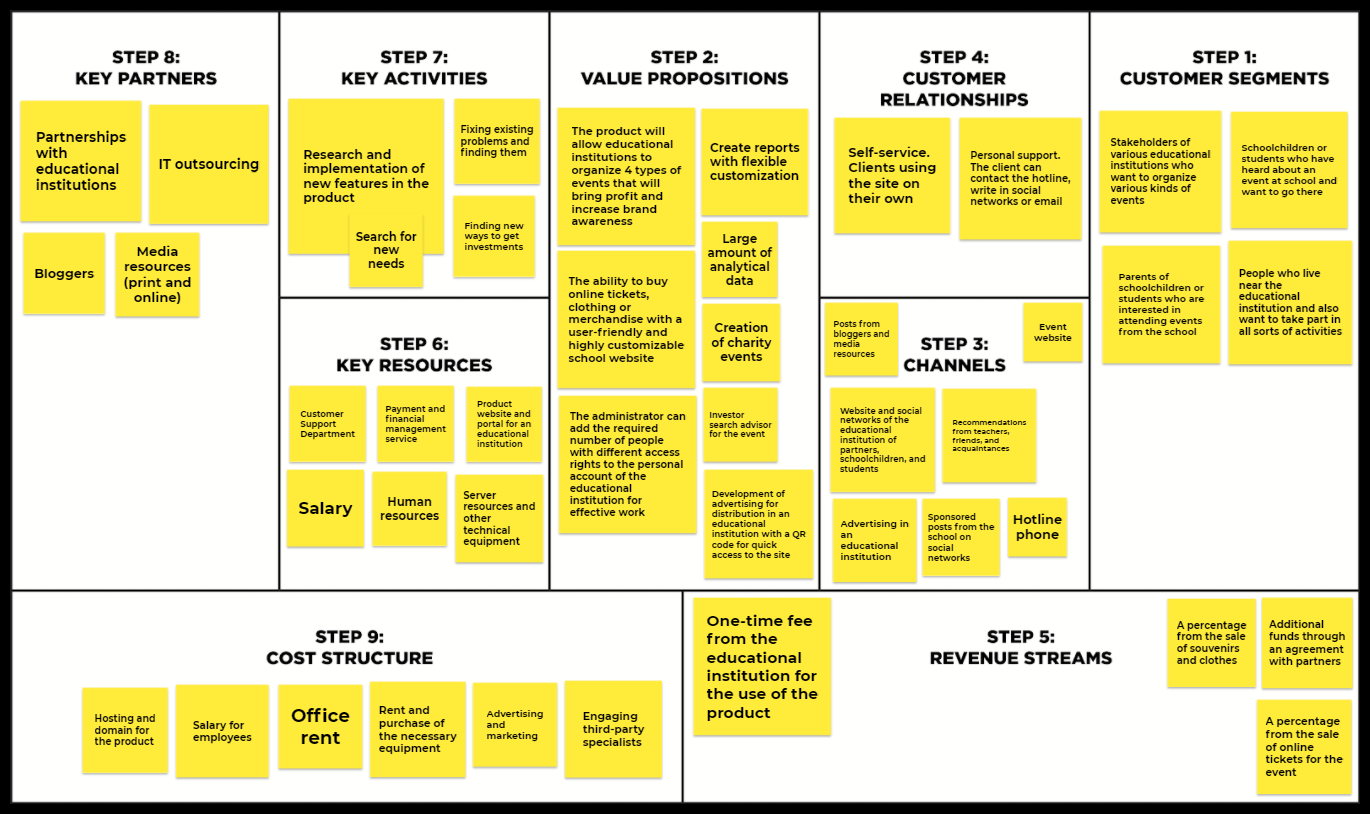
Step 1: Customer segments
The most important block. It identifies different groups (types) of people or organizations that the business wants to attract and serve in the future. It can also be explained that the customer segment is those with whom the business works or wants to work. In other words, it is a certain group of people who are united by a common problem or need. Consumers are the basis for the company’s profits, and nothing will work without them. So the better the business describes this segment, the easier it will be to sell a valuable product for this segment or several segments.
There are different types of customer segments:
- Mass. A business model that is focused on the mass market without division into customer segments.
- Niche market. Their goal is to satisfy specific customer segments.
- Segmented. Identify market segments with needs and problems.
- Diversified. Serve 2 related customer segments with different needs and problems.
- Multilateral. Serve 2 or more customer segments.
In this block you need to think about:
- Who are you creating this product or service for?
- Who is your target audience?
- Who will pay for the product or service?
- Who will look for your product or service?
You can create a business model canvas based on a proto-persona. This artifact must be constantly updated. Be sure to review and refine the business model after real interviews with future users.
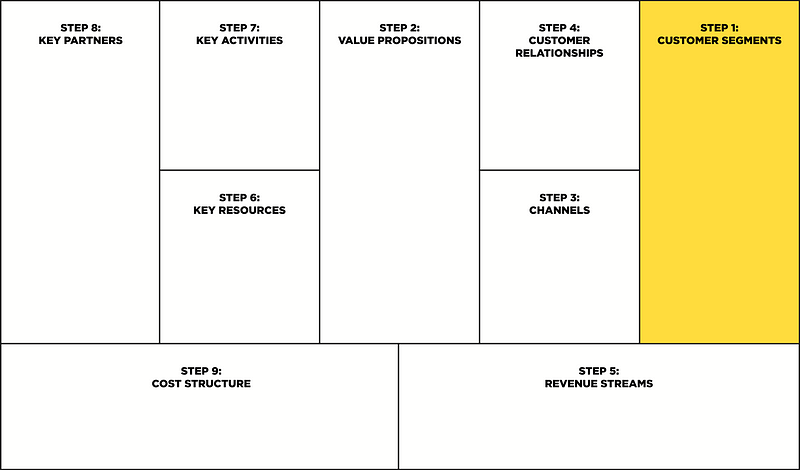
Step 2: Value propositions
This is a logical extension of the customer segment, and this block describes a specific list of products or services that offer value to a specific customer segment. A value proposition is a very reason why customers choose your company over another and buy a product or service only from you. In other words, if the value proposition solves the problems of the customer segment, then you assign the value correctly.
A value proposition creates value for a customer segment by combining certain factors, such as:
- Novelty.
- Productivity.
- Customization.
- Design.
- Brand.
- Status.
- Price.
- Cost reduction.
- Accessibility.
- Utility.
- Convenience for customers.
In this block you need to think about:
- What exactly is the value of your product or service for your customer service?
- What customer service issues or problems are solved by your product or service?
- What are the differences from others?
Step 3: Channels
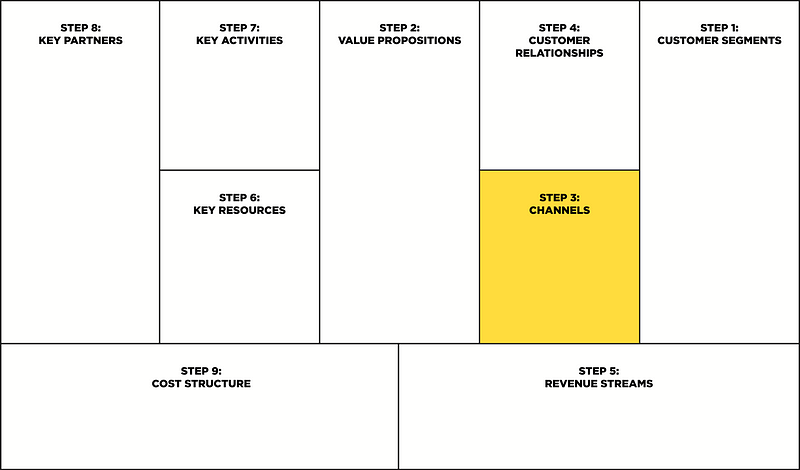
At this stage, we need to understand how we will communicate (interact) with our customer segments to offer and give them a value proposition.
Communication channels have 5 different phases:
- Awareness or information. How do we convey to them our value proposition?
- Rating. How can we help choose our value proposition and bypass competitors?
- Buying or selling. How our products or services are purchased.
- Delivery. How do we deliver our value proposition and form a positive impression on them?
- After-sales period. How will we provide after-sales support?
In this block you need to think about:
- What communication channels do your customer segments want and use now?
- Which communication channels are the most profitable and effective?
Step 4: Customer relationships
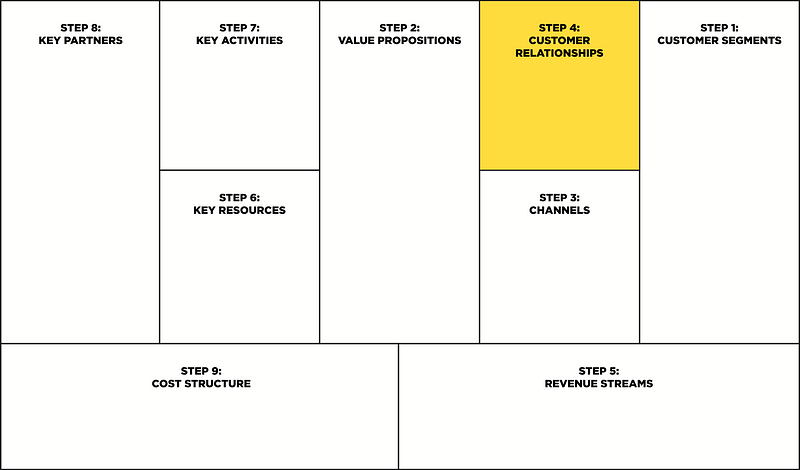
The result of all the previous stages is the fact that there is a certain relationship with our customer segment. This block describes the types of relationships a company establishes with specific customer segments.
There are several categories of customer relationships:
- Personal support. Based on human interaction.
- Special personal support. The special representative is assigned to the client.
- Self-service. Does not support any direct interaction with the client.
- Automated services. This is self-service using automated processes.
- Communities. Online platforms, where customers can share knowledge and solve each other’s problems.
- Co-creation. This attracts customers to the business, intending to create value for your product or service with them.
In this block you need to think about:
- What type of relationship does each of your customer segments expect to receive?
- What types of relationships are already established, and what are the costs?
- What types of relationships are embedded in the overall business model scheme?
Step 5: Revenue streams
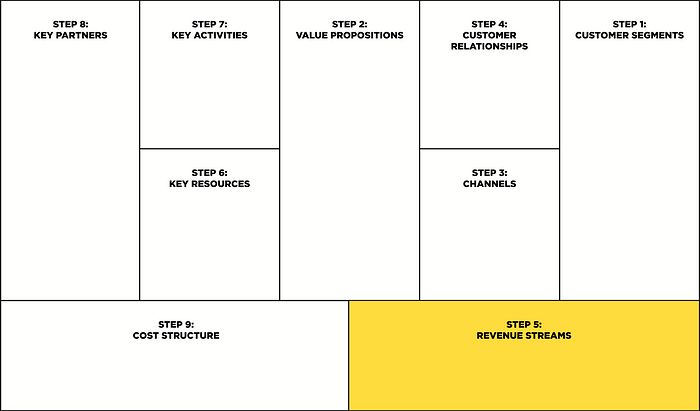
This is our monetization model, ie the funds (profit) that the company earns from each customer segment.
There are several ways to earn an income:
- Sale of assets. Sale of ownership of a physical product.
- Usage fee. Provision of a service for which the client will regularly pay.
- A subscription fee. A subscription to a service with a regular fee for it.
- Lending or rent, or leasing. Temporary use rights.
- Licensing. Permission to use protected intellectual property for money.
- Payment for brokerage services. Intermediary services are provided by 2 or more parties.
- Advertising. Payment for viewing advertising of a product or service.
And also, according to the pricing mechanism, there are:
- Fixed and dynamic. It all depends on the market.
In this block you need to think about:
- What value are our customers willing to pay, and what are they paying for now?
- How do they pay for our product or service?
- What payment methods would they prefer?
- What is the contribution of each customer flow to the company’s total revenue?
Step 6: Key resources

This block describes the most important assets that are needed for a business model to be viable. Your resources are described, allowing the business to develop and communicate value proposals to customers, then maintain connections, and as a result of such a chain generate revenue.
Resources can be classified by:
- Material and technical. This refers to the coverage of physical objects such as manufacturing facilities, various buildings, vehicles, machines, etc.
- Intellectual. These can be brands, confidential information, patents or copyrights, etc.
- Human. They depend on human investment in business because their resources play a high role in some industries.
- Financial. Some business models require financial investments.
In this block you need to think about:
- What key resources are needed for your value proposition?
- What distribution channels, customer relationships, or revenue streams does your business need?
Step 7: Key activities
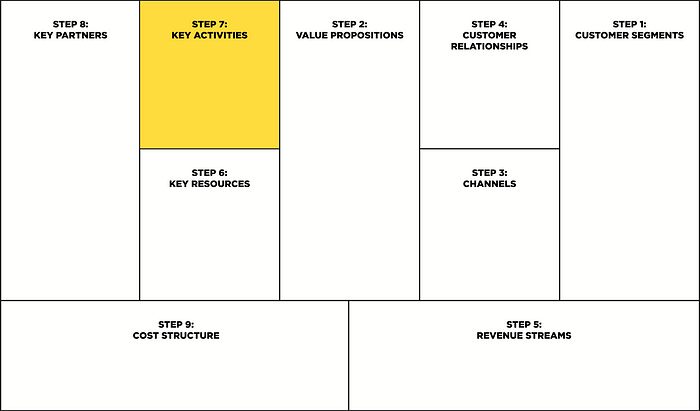
These are the most important actions of the company, which are aimed at creating value, i.e. This block describes the most important events that will help the company to make its business module viable (as a result, we have the necessary value proposals that will allow us to enter the market and offer them to our customer segments to make a profit).
Key activities can be classified:
- Production. Development, manufacture, and distribution of the product on an industrial scale of the highest quality.
- Problem-solving. Solution of individual problems of clients.
- Infrastructure management. Resources are aimed at maintaining and developing a service, platform, or application.
In this block you need to think about:
- What key activities does our value proposition lack?
- Without which ones the company cannot exist?
- What do companies need to do to constantly improve the quality of a product or service?
Step 8: Key partners
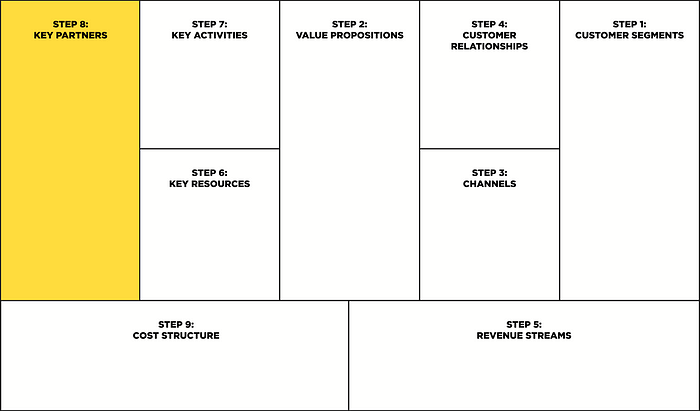
This block describes all suppliers or partners through which the business model works successfully. Companies partner to optimize their business models, reduce risk, or access additional resources.
There are 3 types of motivation to create partnerships:
- Optimization and economies of scale. The main form is designed to optimize actions, namely the supply of value from producer to buyer, which reduces costs.
- Reduce risk and uncertainty. Partnerships can help reduce the risks of a competitive environment.
- Acquisition of certain resources and activities. Involve other firms that provide them with a specific range of resources or even perform certain types of work.
In this block you need to think about:
- Who are our key partners?
- What kind of partnership can reduce our costs, and who can become a partner?
- What types of work can be transferred to our partners without losing the quality of work performed?
- What key resources do we receive and implement with our partners?
Step 9: Cost structure
This is a block that describes all the costs required to operate a business model.
Costs need to be minimized, but they are also distinguished:
- Cost-managed. Focused on minimizing costs.
- Value-driven. In case you prefer value creation and don’t worry so much about costs.
- Fixed costs. Costs that are constant, regardless of the volume of manufactured goods or services.
- Variable costs. They change according to the volume of goods or services produced.
- Economies of scale. Benefits that a business receives as it expands. >Step 9: Cost structure
- Savings at large capacity. These are the benefits that a business gets from its growth.

In this block you need to think about:
- What are the most important costs in our business model?
- Which key resources cost us the most?
- What key activities are the most costly for a business?






